The National Green Tribunal (NGT) has granted clearance to the ₹80,000 crore Great Nicobar Development Project, dismissing petitions that challenged its environmental approval. The decision comes after months of deliberation over what has been described as one of India’s most ambitious and controversial infrastructure initiatives.
A six-member special bench led by NGT Chairperson Justice Prakash Shrivastava concluded that there were no substantial grounds to interfere with the environmental clearance granted to the project in 2022. The tribunal observed that concerns raised during earlier proceedings had been examined by a high-powered committee constituted to reassess the clearance conditions. Taking into account the project’s strategic importance, the bench stated that adequate safeguards had been incorporated.
Strategic Infrastructure in the Indian Ocean Region
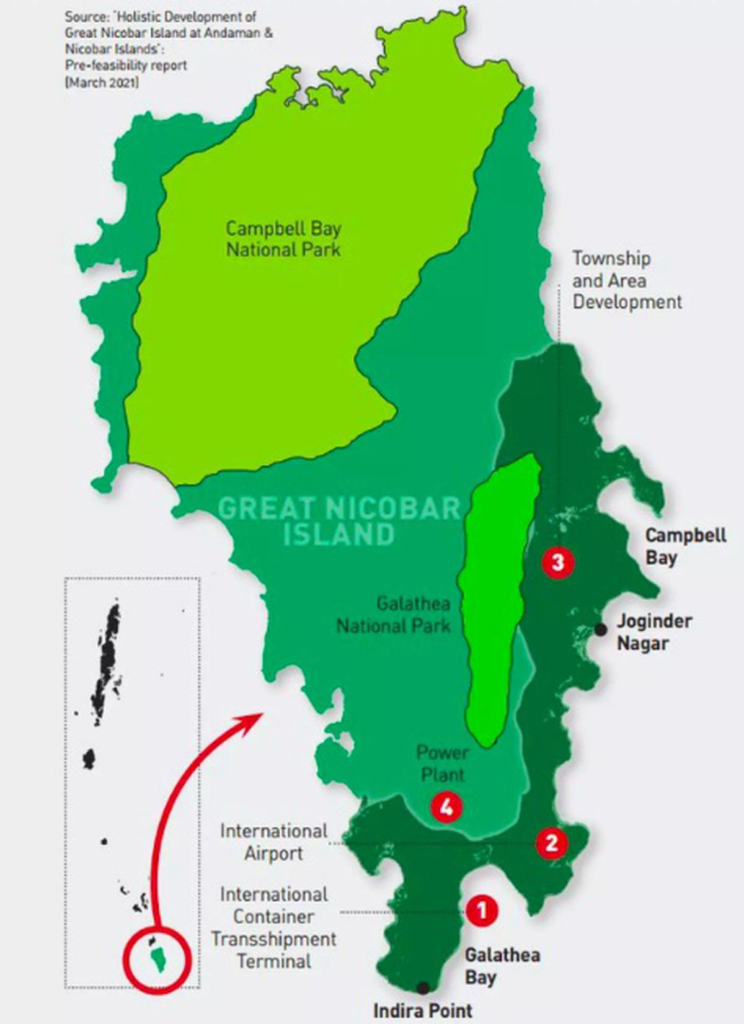
The mega project spans approximately 166 sq km on Great Nicobar Island and involves diversion of nearly 130 sq km of forest land. Key components include a large international transshipment port, a dual-use civil and military airport, and supporting township infrastructure. The development is expected to strengthen India’s strategic footprint in the Indian Ocean Region, particularly amid increasing geopolitical competition.
Environmental and Social Concerns
Despite the approval, the project has drawn strong opposition from conservationists and civil society groups. Environmental experts have cautioned that large-scale forest diversion and coastal construction could significantly impact biodiversity in one of India’s most ecologically sensitive island ecosystems.
Concerns have also been raised regarding the potential displacement and cultural impact on indigenous communities inhabiting the region. Political reactions followed the NGT decision, with the opposition party Indian National Congress describing the clearance as “deeply disappointing” and reiterating warnings about ecological and social risks.
The Road Ahead
With judicial challenges now disposed of, the project moves closer to implementation. However, its execution will likely remain under scrutiny from environmental groups, policy analysts, and strategic experts alike. The Great Nicobar Project thus represents not only an infrastructure milestone but also a test case in balancing ecological preservation, indigenous rights, and national strategic ambitions.
Also Read: Tamsa River Rejuvenation in Azamgarh Becomes Model for Tributary Conservation under Namami Gange
